Sensorineural hearing loss

What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common of the three types of hearing loss (with the other two being conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss).
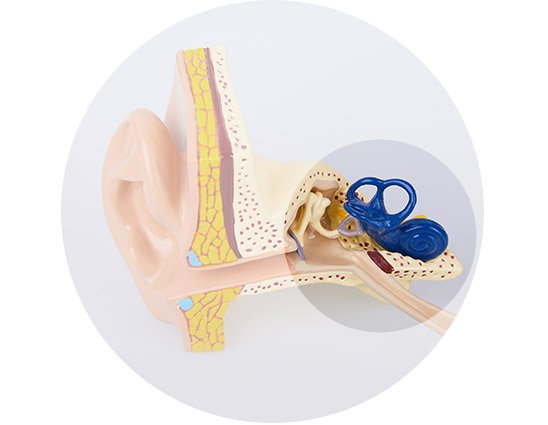
This type of hearing loss implies that the tiny hair cells in the inner ear or the auditory nerve (responsible for transmitting sound to the brain) are damaged. It is most often caused by the natural aging process or exposure to loud sounds1.

Book a FREE* hearing check for sensorineural hearing loss
What causes sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs by damage to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear or the auditory nerve. This can happen due to several causes, including:
- Aging - Age-related hearing loss, which is also called Presbycusis, is the most common form of sensorineural hearing loss
- Exposure to loud sounds, such as a one-time explosion or continuous exposure to loud sounds over time
- Certain drugs and medications
- Genetics or complications during birth and pregnancy
What is sudden sensorineural hearing loss?
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) - known as sudden deafness - involves an unexplained rapid loss of hearing all at once or over a couple of days. It is almost always experienced in one ear only.
In some cases, sudden onset sensorineural hearing loss can be reversed by medical treatment. If you experience sudden hearing loss, visit your doctor for medical advice or call us at 0800 569 152.
6 common signs of sensorinerual hearing loss
It can be difficult to identify the signs and symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss. To help you in the process, below are 6 common signs of sensorineural hearing loss:

How is sensorineural hearing loss treated?
Sensorineural hearing loss can most often be treated with hearing aids. There are a wide variety of hearing aids available, with plenty of options to suit your needs and preferences. More severe sensorineural losses may benefit from medically implantable devices.
We recommend that you receive treatment as early as possible since sensorineural hearing loss can have unwanted side effects, such as decrease in life quality and loneliness.
Prevent hearing loss before it impacts you or a loved one
Even if you don't currently have symptoms of hearing loss, you can still be proactive in preventing it. Using hearing protection, such as ear plugs, molds or earmuffs, is one effective way to prevent hearing loss. Wearing this protective gear will help to protect your ears from especially loud sounds, such as :
- Garden tools like lawn mowers and leaf blowers
- Woodworking machinery
- Loud appliances
- Work-related exposure, including factories and construction sites
- Snowmobiles
- Music
Excessively loud everyday sounds, both at home and at work, can pose a risk to your hearing health, so it's a good idea to invest in hearing protection if you expect to be exposed to loud noise. Avoiding loud sounds and reducing exposure can be beneficial for your longterm hearing health.
Sources
1. https://www.healthyhearing.com/report/50276-Common-causes-of-sensorineural-hearing-loss
2. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003291.htm









